Microsoft Suite Server Operating Systems
- Windows Server 2012
-

With Windows Server 2012, Microsoft delivers a server platform built on our experience of building and operating many of the world's largest cloud-based services and datacentre. Whether you are setting-up a single server for your small business or architecting a major new datacentre environment, Windows Server 2012 will help you cloud-optimize your IT so you can fully meet your organization's unique needs.
- New Server Manager - Create and manage server groups
- Better edition and SKU Selection
- A command-line first, GUI second mentality
- Hyper-V replication
- Expanded PowerShell capabilities
- Storage Spaces - Flipping complexity on its head
- Direct Access - A VPN without the pain of a VPN
- Dynamic Access Control - New way of thinking
- Resilient File System - An evolution of NTFS
- Out-of-the-box IP address management
Metro or Core? Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 will be 64-bit only and can be installed without graphical user interface (GUI), and with a minimal set of server roles. PowerShell is the preferred command management interface with a vast number of ready-made cmdlets.
If you choose to use the local GUI you will experience the Metro front end as shown below.
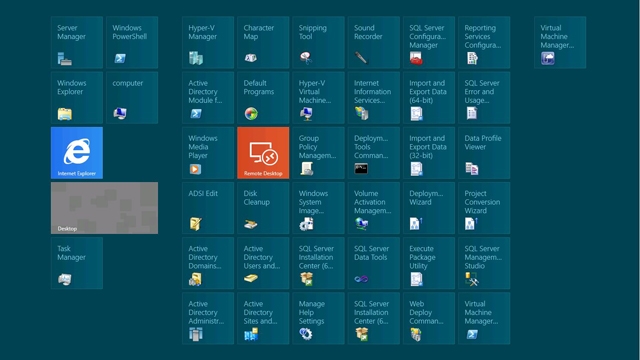
New Windows Server 2012 Management
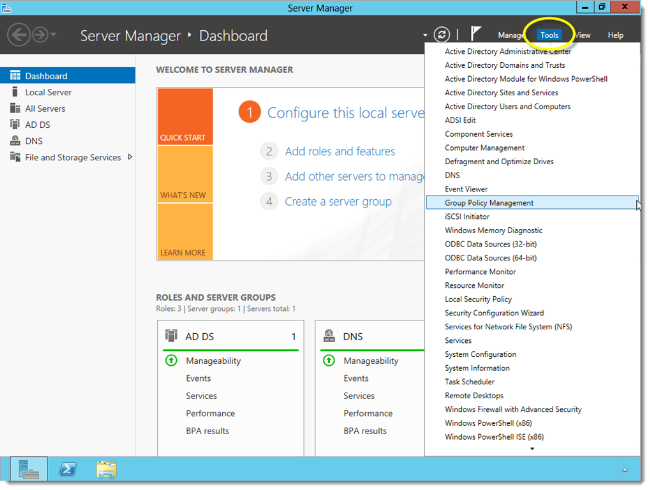
The new and updated Server Manager also has the ability to manage remote and group servers, and perform the same task on all members of a group at once. Windows Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) have also been enhanced to compliment the new Operating System.
Windows Server 2012 – Hyper-V 3
One of the big enhancements is the new and improved Hyper-V hypervisor. Virtual machines can support for up to 64 virtual processors and 1TB of virtual memory per VM. There’s also a new virtual disk format (VHDX) to give VMs access to 64TB of storage. Hyper-V 3.0 can handle up to 160 processors/cores and 2TB of RAM, sharing these resources across 1,024 VMs.
There is also the addition of support for multiple live migrations, bringing Hyper-V up to a similar level of functionality as vSphere.

Windows Server 2012 Editions

The Windows Server 2012 licensing has been streamlined and simple choice Standard and Datacentre editions has minimised licensing complexity.
Iconic have already performed live Domain Migrations to Windows Server 2012 and case studies will be available soon.
- Windows Server 2008 R2
-

Windows Server 2008 R2 builds on the award-winning foundation of Windows Server 2008, expanding existing technology and adding new features. Just a few of the enhancement in this release include new virtualization tools consisting of an updated version of Hyper-V with Live Migration and Dynamic Memory, Remote Fx in Remote Desktop Services, improved power management, and added features with Windows 7 integration such as BranchCache and Direct Access.
Iconic have performed many implementations and migrations to Windows Server 2008 R2 and also with the following server technologies
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows Server 2003
- Windows Server 2000
- Windows NT 4
Windows Server 2008 R2, now with Service Pack 1 (SP1) provides new virtualization technology that enables you to deliver more advanced capabilities to your business for increased IT efficiency and agility. Whether you want to consolidate servers, build a private cloud or offer Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, the addition of these powerful virtualization features enables you to take your datacenter and desktop virtualization strategy to a new level.
Windows 2008 R2 - Robust Features for Optimum Flexibility
Windows Server 2008 R2 with SP1 is a platform server that includes a robust set of features. Whether you want to consolidate servers, build a Microsoft private cloud, or offer Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, the features of Windows Server 2008 R2 with SP1 offer you the flexibility to deliver advanced capabilities to your business for increased IT efficiency and agility.
Key Features
Virtualization with Hyper-V
Hyper-V, a platform technology improved in Windows Server 2008 R2 with SP1 virtualizes the system resources of a physical computer, allowing you to provide a virtualized environment for operating systems and applications. You can optimize your server hardware investments by consolidating multiple server roles as separate virtual machines running on a single physical machine. This allows you to run multiple different operating systems in parallel, on a single server. Or can you use Hyper-V to build out a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) which enables a rich Windows experience for virtual desktops while enhancing security, regulatory compliance and manageability of your desktop environment.
Remote Desktop Services and RemoteFX
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a centralized desktop and application platform that uses session virtualization and VDI technologies to deliver and manage corporate desktops while offering a rich end user experience. RDS accelerates and extends desktop and application deployments to any device, improving remote worker efficiency, while helping keep critical intellectual property secure and radically simplify regulatory compliance. With Microsoft RemoteFX, Windows Server 2008 R2 with Service Pack 1 introduces a new set of remote user-experience capabilities that enable a media-rich user environment for virtual and session-based desktops. RemoteFX can be deployed to a range of thick and thin client devices, enabling cost-effective, local-like access to a media-rich desktop environment. RemoteFX also supports a broad array of USB peripherals to improve the productivity of users of virtual desktops.
Server Management
Ongoing management of servers in the datacenter is one of the most time-consuming tasks facing IT professionals today. Inefficient servers can drive up energy usage and costs. Windows Server 2008 R2 with SP1 delivers features in Server Manager to reduce your administrative effort for common day-to-day operational tasks.
Data Management
Storage requirements today are growing at exponential rates with companies digitizing their content and having to store more unstructured data.
Organizations need to manage their data more effectively as well as more efficiently. Only by gaining insight into their data can companies reduce the cost of storing, maintaining, and managing data. Windows Server 2008 R2 File Classification Infrastructure (FCI) provides insight into your data by automating classification processes so that you can manage your data more effectively and economically. FCI does this by enabling to automatically classify files based on properties defined by administrators (such as whether or not a file contains personally identifiable information) and performing administrator-specified actions based on that classification (backing up files containing personal information to an encrypted store, for example). These mechanisms are included in the box as well as provided by extensible interfaces that allow IT organizations and partners to build rich end to end solutions for classifying and applying policy based on classification. FCI helps customers save money and reduce risk by managing files based on their business value and business impact.
Web Application Platform
Windows Server 2008 R2 includes many enhancements that enable you to more easily deploy and manage web applications. It offers an updated Web server role, Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.5, and greater support for .NET on Server Core. Additionally, IIS 7.5 provides a security-enhanced, easy-to-manage platform for developing and reliably hosting Web applications and services. By providing more control, more choice, more reliability, and more security, organizations can ensure their Web platforms are available whenever and wherever they are needed.
Scalability & Reliability
Windows Server 2008 R2 is capable of unprecedented workload size, dynamic scalability, and across-the-board availability, and reliability. A host of new and updated features are available, including leveraging sophisticated CPU architectures, increased operating system componentization, and improved performance and scalability for applications and services.
Integrated Experience with Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2 with SP1 has many features that are designed specifically to work with client computers running Windows 7, Microsoft’s most current version of the Windows client operating system.
BranchCache
The BranchCache feature in Windows Server 2008 R2 reduces WAN utilization and improves the responsiveness of network applications. BranchCache in the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 operating systems can help increase network responsiveness of centralized applications when accessed from remote offices, giving users in those offices the experience of working on your local area network. BranchCache also helps reduce wide area network (WAN) utilization.
Direct Access
Direct Access is a feature in the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 operating systems that gives users the experience of being seamlessly connected to their corporate network any time they have Internet access. With Direct Access, users are able to access corporate resources, such as e-mail servers, shared folders, or intranet Web sites, securely without connecting to a virtual private network (VPN).
- Microsoft Core Network Components
-

Active Directory provides the means to manage the identities and relationships that make up your organization's network.
Iconic have vast experience in implementation, migration and integration of all of these key Microsoft Network Components and below is just a small selection of what we can do.
Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory provides the means to manage the identities and relationships that make up your organisation's network. Active Directory gives you out-of-the-box functionality needed to centrally configure and administer system, user, and application settings. Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) stores directory data and manages communication between users and domains, including user logon processes, authentication, and directory searches
Active Directory Rights Management
Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) and the AD RMS client, enable you to augment an organisation's security strategy by protecting information through persistent usage policies, which remain with the information, no matter where it is moved. You can use AD RMS to help prevent sensitive information-such as financial reports, product specifications, customer data, and confidential e-mail messages-from intentionally or accidentally getting into the wrong hands.
Active Directory Federation Services
Active Directory Federation Services is a highly secure, highly extensible, and Internet-scalable identity access solution that allows organisations to authenticate users from partner organizations. Using AD FS in Windows Server 2008 R2 and later, you can simply and very securely grant external users access to your organization's domain resources. AD FS can also simplify integration between untrusted resources and domain resources within your own organization
Active Directory Certification Services
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) enhances security by binding the identity of a person, device, or service to their own private key. Storing the certificate and private key within Active Directory helps securely protect the identity, and Active Directory becomes the centralized location for retrieving the appropriate information when an application places a request.
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Service (AD LDS), formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode, can be used to provide directory services for directory-enabled applications. Instead of using your organization's AD DS database to store the directory-enabled application data, AD LDS can be used to store the data. AD LDS can be used in conjunction with AD DS so that you can have a central location for security accounts (AD DS) and another location to support the application configuration and directory data (AD LDS).
DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical, distributed database that contains mappings of DNS domain names to various types of data, such as Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS allows you to use friendly names, such as www.microsoft.com, to easily locate computers and other resources on a TCP/IP-based network.
DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard designed to reduce the administration burden and complexity of configuring hosts on a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)-based network, such as a private intranet.
By using DHCP server computers to centrally manage IP addresses and other related configuration parameters, using DHCP client computers to request and accept TCP/IP configuration information from DHCP servers, and using DHCP relay agents to pass information between DHCP clients and servers, the process of configuring TCP/IP on DHCP clients is automatic.
Group Policy
Group Policy is an infrastructure that allows you to specify managed configurations for users and computers through Group Policy settings and Group Policy Preferences. For Group Policy settings that affect only a local computer or user, you can use the Local Group Policy Editor. You can manage Group Policy settings and Group Policy Preferences in an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) environment through the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). Group Policy management tools also are included in the Remote Server Administration Tools pack to provide a way for you to administer Group Policy settings from your desktop.
Network Load Balancing
The Network Load Balancing (NLB) feature in Windows Server Systems distributes traffic across several servers by using the TCP/IP networking protocol. By combining two or more computers that are running applications in Windows Server into a single virtual cluster, NLB provides reliability and performance for web servers and other mission-critical servers.
The servers in an NLB cluster are called hosts, and each host runs a separate copy of the server applications. NLB distributes incoming client requests across the hosts in the cluster. You can configure the load that is to be handled by each host. You can also add hosts dynamically to the cluster to handle increased load. NLB can also direct all traffic to a designated single host, which is called the default host.
NLB allows all of the computers in the cluster to be addressed by the same set of IP addresses, and it maintains a set of unique, dedicated IP addresses for each host. For load-balanced applications, when a host fails or goes offline, the load is automatically redistributed among the computers that are still operating. When it is ready, the offline computer can transparently rejoin the cluster and regain its share of the workload, which allows the other computers in the cluster to handle less traffic.
Windows Server Update Services
The Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) enables information technology administrators to deploy the latest Microsoft product updates. By using WSUS, administrators can fully manage the distribution of updates that are released through Microsoft Update to computers in their network.
Windows Deployment Services
Windows Deployment Services (WDS) enables you to deploy Windows operating systems over the network, which means that you do not have to install each operating system directly from a CD or DVD
If you would like to find out more about how Iconic IT can help your business with our consultancy services then please contact us today on 0330 088 3338.
